What is a Spinal Tap?
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: February 2018 | Last updated: February 2022
A spinal tap, also called a lumbar puncture, is a procedure that tests the fluid that flows around the spinal cord and brain, called the cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid is tested to see if blood cancer has spread to the central nervous system (CNS), as certain blood cancers can potentially spread to the CNS. The test is named for the lumbar region of the back, which is the lower back and where the test is performed.1,2
In addition to diagnosing and staging some blood cancers, a spinal tap may be performed to test for serious infections like meningitis, other conditions that affect the CNS like multiple sclerosis, or other cancers that can affect the brain or spinal cord.2
What to expect during the test
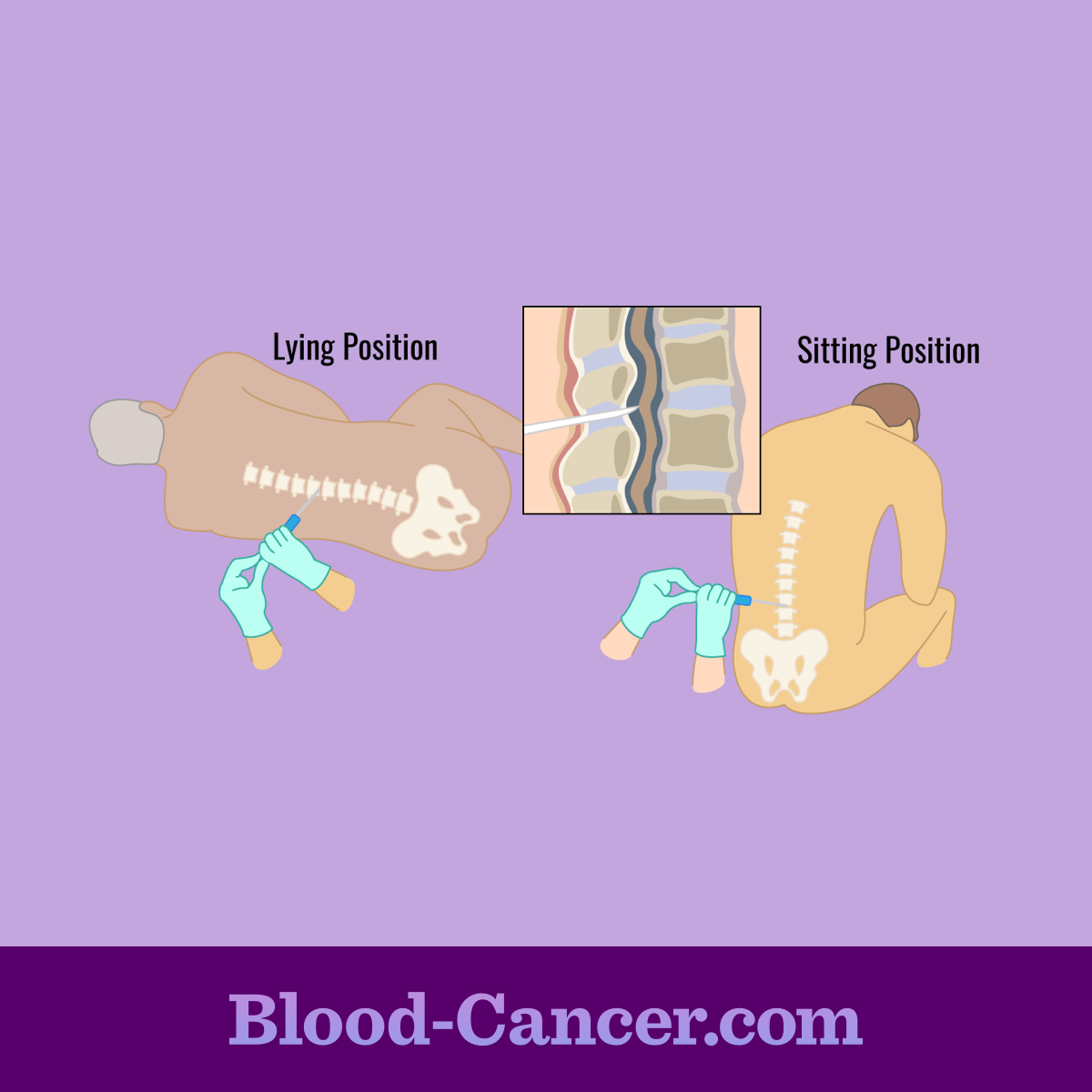
To get a sample of the cerebrospinal fluid, the patient is asked to lie on their side with their knees pulled up to their chest, or they may be asked to sit and lean forward over a stable surface, like a table. These positions allow for better access to the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spine. The spinal tap is generally done between the 3rd and 4th vertebrae in the lumbar region.1,2
Figure 1. Spinal tap
Before removing a sample of fluid, the patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area. After the anesthetic has taken effect, a thin needle is inserted into the space between the lumbar vertebrae and a small amount of fluid is removed. The puncture site will be covered with a bandage.2
Following a spinal tap
After the procedure, the patient may be asked to lie down for a while. The patient should not engage in strenuous activity or exercise for the rest of the day, although some people can return to work, if their work isn't physically active. Some people find an over-the-counter pain medication may be helpful for headache or back pain that may occur, although patients should always consult with their individual doctor for specific medical advice, and medication instruction, before taking any over-the-counter products.2
Results of a spinal tap
The sample of fluid is sent to the laboratory for examination to measure several characteristics, including:
- Color and clarity - spinal fluid is normally clear and colorless; a cloudy or yellow appearance could indicate infection
- Levels of protein - high levels of certain proteins may indicate infection
- White blood cells (WBCs) - while spinal fluid normally contains some WBCs, a higher than normal level could indicate infection
- Glucose (sugar) - low glucose levels can indicate infection or other conditions
- Cancer cells - the presence of cancer cells or immature blood cells can indicate certain kinds of blood cancer or other cancers2
The results are usually communicated by the doctor within a few days of the procedure.2